Nvidia Announces ‘DRIVE Map', a High-Definition, Mapping Platform for Autonomous Vehicles Using Crowdsourced Data
【Summary】Nvidia CEO and founder Jensen Huang announced the new DRIVE Map platform during his keynote at Nvidia’s annual GTC technology conference on Tuesday. The company plans to map hundreds of thousands of miles of roadways in the US, China and Europe to help autonomous vehicle safety navigate with accuracy of 5 centimeters or less.

What if you can build 3D road maps with centimeter-level accuracy? It's what chipmaker Nvidia Corp has done with its new NVIDIA DRIVE Map platform. The company plans to map hundreds of thousands of miles of roadways in the US, China and Europe to help autonomous vehicle safety navigate with accuracy of 5 centimeters or less.
Nvidia CEO and founder Jensen Huang announced the new DRIVE Map platform during his keynote at Nvidia's annual GTC technology conference on Tuesday.
DRIVE Map is a scalable, multi-modal mapping engine designed to accelerate the deployment of Level-3 and even Level-4 autonomous vehicles, which are being built to operate without human intervention. To achieve higher levels of autonomy, these vehicles require much more detailed maps in order to safely navigate without human assistance.
Nvidia accelerated the development of DRIVE Map after it acquired HD mapping startup DeepMap last year. The startup's core mapping technologies were rolled into DRIVE Map. Nvidia's DRIVE Map combines the accuracy of DeepMap survey mapping, but with the scale of AI-based crowdsourced mapping.
Before the company was acquired by Nvidia, DeepMap specialized in fusing crowdsourced images from digital cameras, radar and 3D lidar data collected from passenger vehicles to create its high definition maps for self-driving vehicles.
Ride-hailing company Lyft Inc also experimented with using crowdsourced data to build highly accurate HD maps. In 2020, some drivers on Lyft's ride-hailing platform started using small, low-cost dash cameras to collect footage of intersections, bicyclists, pedestrians, as well as the behavior of other drivers while the driver is out and about picking up passengers.
The HD Maps used by self-driving vehicles include semantic details not found on standard 2D maps used by millions of drivers everyday for turn-by-turn driving directions. Whereas highly detailed 3D maps include the exact position of lane markings, road signs, crosswalks, curbs and other infrastructure.
DeepMap's other work focused on keeping these maps up to date using the crowdsourced data it collected from vehicles, as well as keeping them readily available. Keeping HD maps updated and accessible in real-time has been a big challenge for developers of self-driving vehicles.
Nvidia's DRIVE Map is designed to support autonomous vehicles everywhere in the world. NVIDIA is creating HD maps of major highways in North America, Europe, and Asia. It will provide survey-level ground truth mapping coverage to 500,000 kilometers (310,600 miles) of roadways in North America, Europe and Asia by 2024. The maps will be continuously updated and expanded with data collected from millions of passenger vehicles.
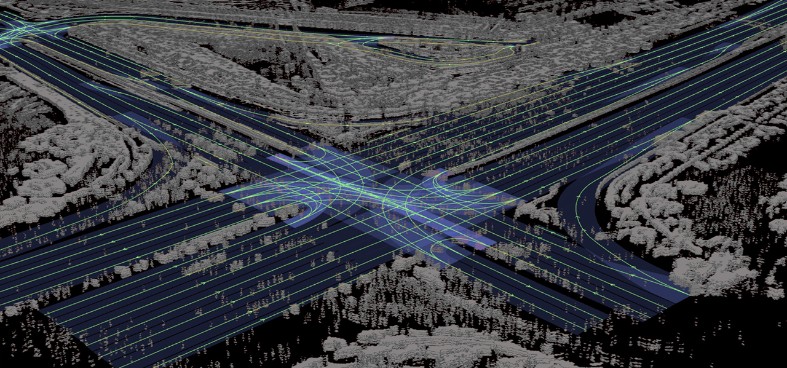
DRIVE Map details generated using radar scans.
Three Map Layers, Camera, Radar and Lidar
The multi-layered DRIVE Map contains localization layers for cameras, radars and lidar sensors, so an autonomous vehicle's GPS can know precisely where it is on a map using one or more of the three layers. The AI-powered map driver can localize to each layer of the map independently, providing the added redundancy required for SAE Level 3 and 4 autonomous driving.
The camera localization layer consists of the same details that human drivers see when navigating, such as lane dividers, road markings, road boundaries, traffic lights, signs and utility poles.
The radar localization layer of the map is an aggregate point cloud of radar returns which is also used to determine an autonomous vehicle's precise location. The radar data is particularly useful in low light conditions and poor weather conditions such as rain or fog, where cameras and lidar do not perform as well.
Using radar for localization is also helpful in suburban areas where typical map attributes aren't always available, enabling the AI driver to localize based on surrounding objects picked up by radar scans.
The lidar voxel layer provides the most precise and reliable representation of the environment. It builds a 3D representation of the world at 5-centimeter resolution, according to Nivida. The company says that this high level of accuracy is impossible to achieve with camera and radar data alone.
Once a vehicle is precisely located on the map, the AI can use the detailed semantic information in the map to center the vehicle in a lane and drive in a way that other road users expect.
Semantic map data includes features such as road layouts, turn-only lanes, pedestrian crosswalks and traffic lights, as well as how all of the features interconnect for navigating. Its similar to how human drivers navigate using GPS with turn-by-turn directions.
DRIVE Map is actually built using two seperate map engines, a ground truth survey map engine and crowdsourced map engine. The ground truth data is collected from survey vehicles, while the crowdsourced map engine is built from data collected from passenger vehicles that travel though the mapped areas.
This approach achieves centimeter-level accuracy with dedicated survey vehicles, as well as the freshness and scale that can only be achieved with millions of passenger vehicles continuously updating and expanding the map with real world data.
The ground truth engine is based on the DeepMap survey map engine technology, which has been developed and verified over the past six years.
The AI-based crowdsource engine gathers map updates from millions of cars, constantly uploading new data to the cloud as the vehicles drive. The data is then aggregated at full fidelity in NVIDIA Omniverse and used to update the map, providing the real-world fleet fresh over-the-air map updates within hours.
DRIVE Map also provides a data interface called "DRIVE MapStream", to allow any passenger car that meets the DRIVE Map requirements to continuously update the map using camera, radar and lidar data collected from the vehicle.
An Earth-Scale ‘Digital Twin'
In addition to assisting the AI-powered autonomous driving systems to make better driving decisions, DRIVE Map will help to accelerate autonomous vehicle deployment by generating ground-truth training data for deep neural network (DNN) training, as well as for testing and validation purposes.
These workflows are centered on Nvidia Omniverse, where the real-world map data is loaded and stored. Omniverse maintains this Earth-scale representation of the digital twin, which will be continuously updated using survey map vehicles along with millions of passenger vehicles.
For developers of autonomous vehicles. Omniverse includes automated content generation tools, so that the detailed map can be converted into a drivable simulation test environment that can be used with NVIDIA DRIVE Sim to improve AI-powered autonomous driving software. Features such as road elevation, road markings, islands, traffic signals, signs and utility poles are accurately replicated in the simulation environment at centimeter-level accuracy, according to Nvidia.
Nvidia developed a powerful computer simulation environment that provides autonomous technology developers an "artificial universe" to train robotaxis and self-driving vehicles how to drive in the real world in a simulated environment that's built using real world data.
Developers of self-driving vehicles can also use the simulated environment to generate edge-case training scenarios that aren't available from real-world data or are difficult to obtain using survey vehicles.
AV developers can also test their software in the safety of the digital twin environment before deploying autonomous vehicles in the real world.
The digital twin provides fleet operators a complete virtual view of where the vehicles are driving in the world, assisting with remote operation when needed.
The new DRIVE Map is a highly versatile and scalable platform from Nvidia. It equips autonomous vehicles with a deep understanding of the real world, which can help developers to improve a vehicle's AI-powered autonomous driving capabilities.
Nvidia said that DRIVE Map will be available to the entire autonomous vehicle industry.
-
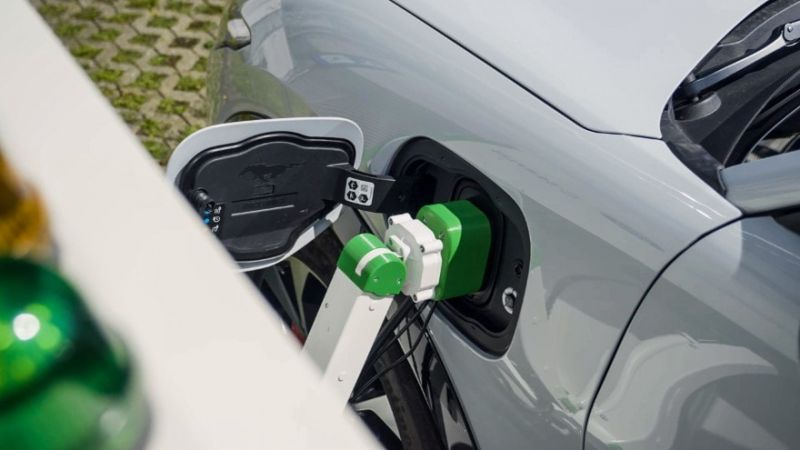


Ford is Testing a New Robotic Charging Station to Assist Drivers of EVs With Disabilities
-
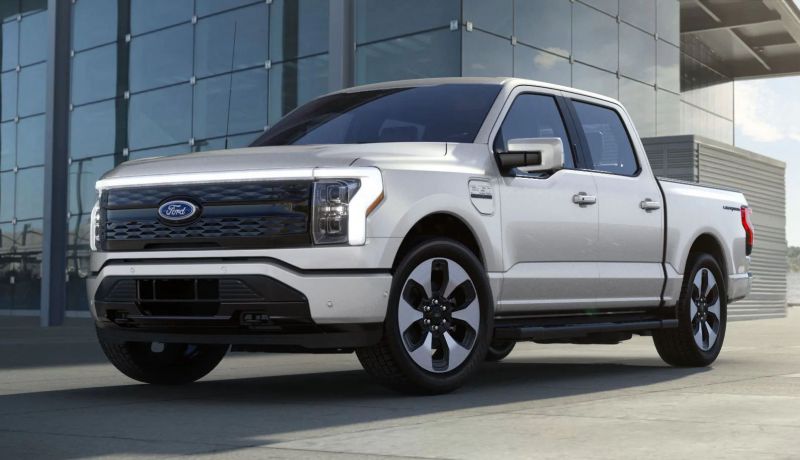


Ford Raises the Prices of the F-150 Lightning Electric Pickup Due to Rising Raw Material Costs
-


The BMW 7-Series to Feature HD Live Maps From HERE Technologies for Hands-Free Highway Driving in North America at Speeds up to 80 MPH
-


AutoX to Use the 'Eyeonic Vision Sensor' from California-based SiLC Technologies for its Robotaxi Fleet in China
-
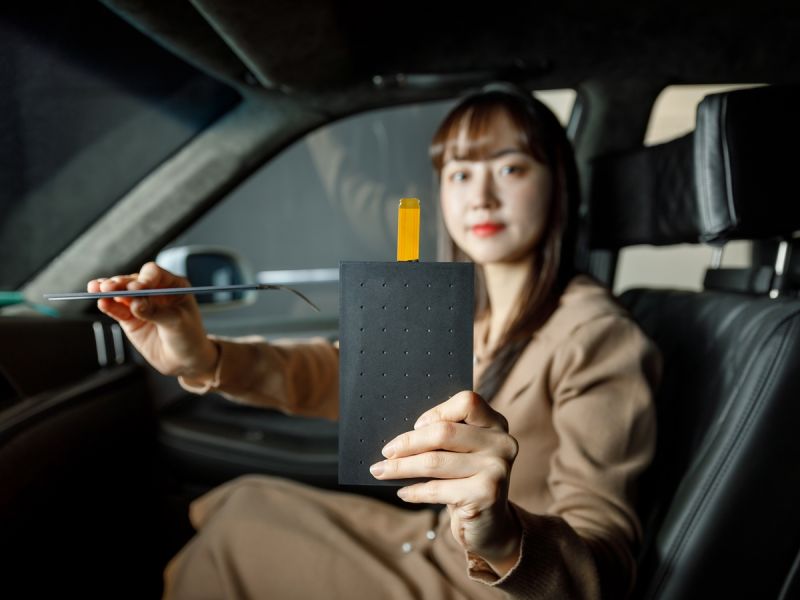


LG Develops ‘Invisible’ Speaker Sound Technology That Could Revolutionize In-Vehicle Audio
-


Researchers at South Korea’s Chung-Ang University Develop a ‘Meta-Reinforcement’ Machine Learning Algorithm for Traffic Lights to Improve Vehicle Throughput
-


Zeekr’s New 009 Electric Passenger Van is the World’s First EV to Feature CATL’s Advanced ‘Qilin’ Battery With a Range of 510 Miles
-


Redwood Materials is Building an Electric Vehicle Battery Recycling Facility in South Carolina
- Mercedes-Benz Signs MoU With the Government of Canada to Source the Raw Materials for Electric Vehicle Batteries
- Valeo Signs Major Deal with BMW to Supply Advanced Driver Assist Hardware for the Automaker's Forthcoming 'Neue Klasse' EV Platform
- The World’s Biggest Battery Producer CATL Signs MoU with EV Startup VinFast to Develop a ‘Skateboard’ Electric Vehicle Platform
- Tesla’s Model 3 is Reportedly Getting a Redesign to Make it More Appealing as Competition in the EV Segment Grows
- High Gas Prices Aren’t Enough to Sway Consumers to EVs, Autolist Survey Finds
- GM to Invest $81 Million to Hand-Build Cadillac Celestiq in Michigan
- Federal Tax Credit on EVs Still Applies to American-Made Vehicles
- Tesla is Bringing in Engineers From Shanghai to Help Ramp Up Production Capacity at its California Factory
- NHTSA Opens Investigations Into Two New Fatal Tesla Accidents
- Volvo Offers a Sneak Peak of its New Flagship EX90 Electric SUV Ahead of its Upcoming Reveal on Nov 9











 About Us
About Us Contact Us
Contact Us Careers
Careers