Tesla Rival XPeng and Alibaba Cloud Set Up China's Largest Cloud-Based Computing Center to Train Machine Learning Models for Autonomous Driving
【Summary】Electric vehicle manufacturer XPeng Inc, which is becoming one of Tesla’s biggest rivals in China with its high tech EVs, has set up a data center with Alibaba Cloud to train its autonomous driving systems. The cloud-based data center will be used to train XPeng’s machine learning models to improve the autonomous driving capabilities of its vehicles much more quickly.
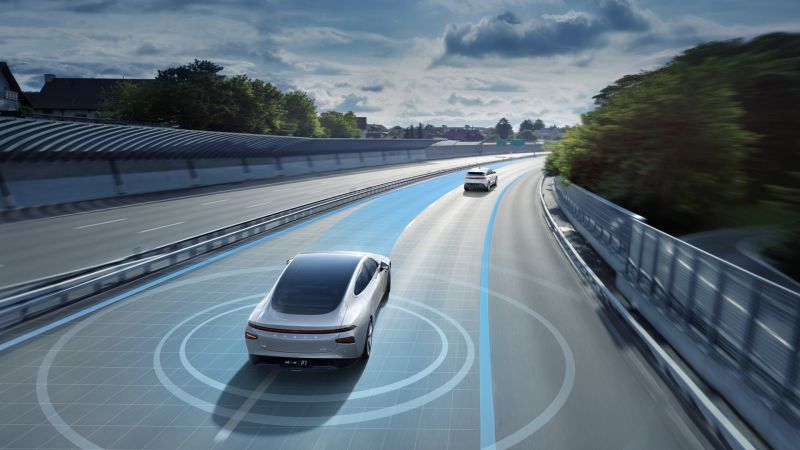

Electric vehicle manufacturer XPeng Inc, which is becoming one of Tesla's biggest rivals in China with its high tech EVs, has set up a data center with Alibaba Cloud to train its autonomous driving systems, Chinese new outlet Gasgoo reports.
The cloud-based data center will be used to train XPeng's machine learning models to improve the autonomous driving capabilities of its vehicles much more quickly. For self-driving cars, machine learning algorithms are an important tool that can be used to predict the behavior of other road users, such as other human drivers, pedestrians and bicyclists.
XPeng and Alibaba Cloud's center offers 600 FLOPS (floating point operations per second) of compute power that can reduce training time of XPeng's autonomous driving algorithms from a week to just one hour, according to the company. With its powerful compute capabilities, the data center will also help to promote the development of advanced Level-3 autonomous driving capabilities in China.
The data center is located in Ulanqab City, which is located around 220 miles west of Beijing. Computer giant Apple Inc. also operates a data center in the city to support its iCloud services for customers in China.
Xpeng's autonomous driving system is called XPILOT and it's offered on the automaker's P7 sedan, which is a strong competitor to the Tesla Model S in China. The latest version of XPILOT brings several autonomous driving features to Chinese customers for the first time, including Level 3 autonomous driving functions for highways, urban roads and automated parking.
The P7 was China's first mass produced electric sedan to come with a 360-degree dual camera and a radar fusion perception system for added safety. The electric sedan is outfitted with 14 cameras, 5 millimeter-wave radars, 12 ultrasonic sensors, lidar, centimeter-level high-definition GPS positioning, decimeter-level high-definition mapping.
In Jan 2021, XPeng unveiled the beta version of its more advanced autonomous driving feature called Navigation Guided Pilot (NGP), which is similar to Tesla's Full Self-Driving (FSD) feature.
Xpeng's NGP is highly advanced and specifically designed for China's complex and crowded road conditions and driving style. The system will follow the route guidance while executing and selecting the optimal route in real-time as well as perform autonomous lane changes.
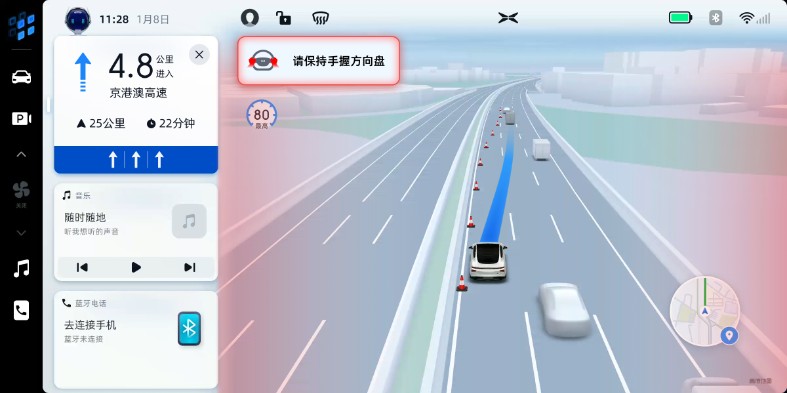
Autonomous driving systems like Xpeng's NGP and XPILOT rely heavily on machine learning algorithms to make better driving decisions over time.
Tesla, for example, continuously collects this type of data from its vehicles remotely, such as when drivers activate its Autopilot automated driving feature. The data collected by Tesla is crunched by machine learning algorithms which are used to make improvements to its autonomous driving software.
However, training these algorithms requires a massive amount of real world data, which is known as "training data". It also requires a tremendous amount of computing power to do these tasks more quickly and efficiently.
Other automakers are also planning using data centers to process data from their vehicles, including Sweden's Volvo Cars. A big part of Volvo's future plans include having ten of thousands of software-powered connected cars on the road in the next decade traveling millions of kilometers and continuously sharing data with the automaker.
All of these software-based vehicles will be like rolling smartphones that can be updated OTA.
To process the massive amount of real-time traffic data collected from Volvo vehicles, Volvo Cars and the automaker's software unit Zenseact are investing in a massive AI-powered data center. The data center can store over 200 Pebibytes (225 million gigabytes) of data.
The crowd-sourced data collected from Volvo vehicles will include continuous inputs from vehicle sensors that monitor the environment, including high-resolution lidar data used for autonomous driving.
By allowing customers to share their vehicle data anonymously, Volvo will be able to continuously make software improvements to its future software-based vehicles, including advanced safety systems and autonomous driving systems. Volvo uses AI and a NVIDIA DRIVE Orin processor installed in the vehicle.
XPeng also uses a Nvidia processor in its P7 sedan. The electric car features the NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Xavier platform to support XPILOT. Nvidia's Xavier SoC is a powerhouse, delivering 30 TOPS (trillions of operations per second) of performance while consuming just 30 watts of power.
Over the past several years, Xpeng has invested heavily in autonomous driving. Roughly half of the company's employees work in R&D of new technology for the electric automaker. Many of these employees work solely on the automaker's autonomous driving technology.
-


Ford is Testing a New Robotic Charging Station to Assist Drivers of EVs With Disabilities
-


Ford Raises the Prices of the F-150 Lightning Electric Pickup Due to Rising Raw Material Costs
-


The BMW 7-Series to Feature HD Live Maps From HERE Technologies for Hands-Free Highway Driving in North America at Speeds up to 80 MPH
-


AutoX to Use the 'Eyeonic Vision Sensor' from California-based SiLC Technologies for its Robotaxi Fleet in China
-


LG Develops ‘Invisible’ Speaker Sound Technology That Could Revolutionize In-Vehicle Audio
-


Researchers at South Korea’s Chung-Ang University Develop a ‘Meta-Reinforcement’ Machine Learning Algorithm for Traffic Lights to Improve Vehicle Throughput
-


Zeekr’s New 009 Electric Passenger Van is the World’s First EV to Feature CATL’s Advanced ‘Qilin’ Battery With a Range of 510 Miles
-


Redwood Materials is Building an Electric Vehicle Battery Recycling Facility in South Carolina
- Toyota’s New ‘Intelligent Assistant’ Learns Voice Commands and Gets Smarter Over Time Using Machine Learning
- The World’s Biggest Battery Producer CATL Signs MoU with EV Startup VinFast to Develop a ‘Skateboard’ Electric Vehicle Platform
- Tesla Rival NIO Inc is Hiring Manufacturing Specialists for a U.S. EV Factory, Reports Say
- SK Inc. Invests $100 Million in North Carolina-based EV Charging Hardware Developer Atom Power
- Polestar Shares the First Image of the Polestar 3 Electric SUV Ahead of its October Debut
- EV Startup NIO to Launch a New Mass-Market Brand to Rival Tesla with an Annual Capacity of 500,000 Vehicles a Year
- Qualcomm and its Industry Partners Demonstrate C-V2X Technology in Georgia That Ensures School Buses and Fire Trucks Never Get Stuck at Red Lights
- The Tesla Model Y and Model 3 Take the 1st and 2nd Place Spots in the Annual Cars.com ‘American-Made Index’
- GM to Invest $81 Million to Hand-Build Cadillac Celestiq in Michigan
- Construction of Panasonic’s New EV Battery Factory in Kansas to Start in November











 About Us
About Us Contact Us
Contact Us Careers
Careers