China's Baidu Reveals the Apollo RT6, a Fully Autonomous, Production Ready Level-4 Robotaxi with Removable Steering Wheel
【Summary】China’s technology giant Baidu Inc, which is the equivalent of Google in its home country, held its “Baidu World 2022” annual tech conference this week which included several major announcements. Among them was the unveiling of Baidu’s production-ready Apollo RT6 robotaxi, a fully autonomous passenger vehicle designed for autonomous urban mobility.

China's technology giant Baidu Inc, which is the equivalent of Google in its home country, held its "Baidu World 2022" annual tech conference this week which included several major announcements. Among them was the unveiling of Baidu's production-ready Apollo RT6 robotaxi, a fully autonomous passenger vehicle designed for autonomous urban mobility.
The Apollo RT6 is the sixth generation of Baudi's autonomous vehicle and was built from the ground up for commercial ride-hailing. It's the first vehicle built on Xinghe, which is Baidu's in-house developed automotive E/E architecture specifically designed for fully autonomous driving.
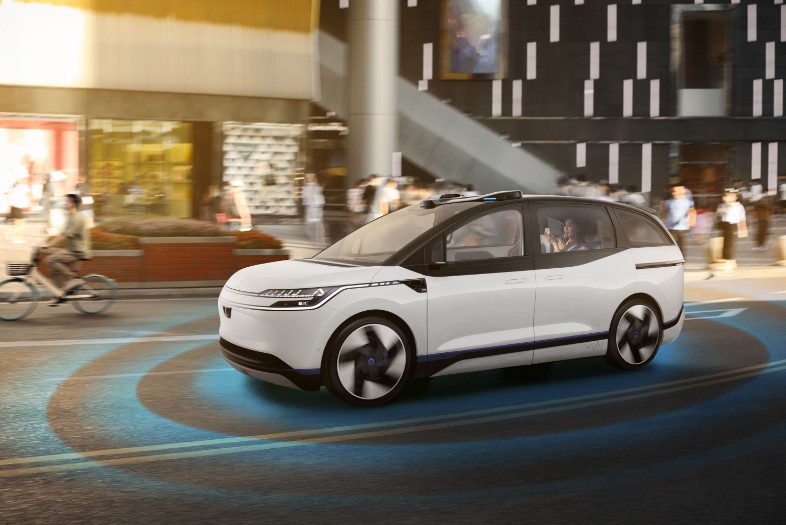

All of the RT6's electrical components and hardware are 100% automotive-grade with full redundancy throughout both hardware and autonomous driving software. The older generations of Baidu's autonomous vehicles were retrofitted from conventional vehicle platforms.
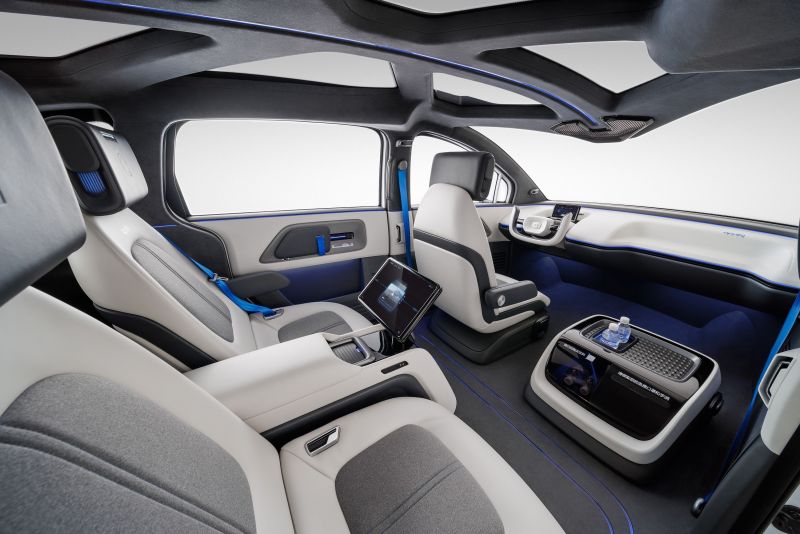
The futuristic RT6, which includes a removable steering wheel to free up additional cabin space, will be used in Baidu's commercial autonomous mobility service Apollo Go. The steering wheel-free design allows for more customization of the interior, such as adding extra seating, desktops, gaming consoles, even a small vending machine where passengers can purchase snacks or drinks.
The vehicle also features intelligent electric sliding doors to further enhance the riding experience.
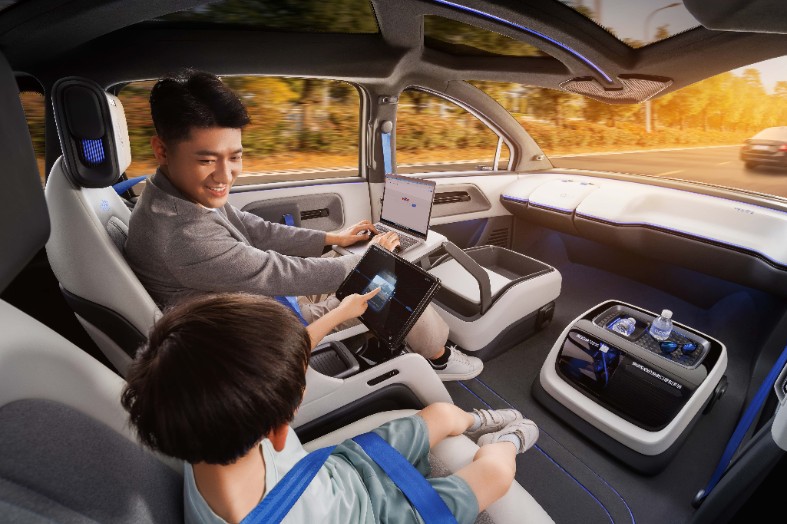

Baidu's Apollo Go service is similar to U.S. ride-hailing companies Uber and Lyft. Riders use an app to summon a driverless Apollo Go vehicle and wait at a nearby station for the vehicle to arrive and pick them up.
The Apollo RT6 is slated to join the Apollo Go ride-hailing service fleet starting in 2023. The number of vehicles on the platform is expected to grow to include ten of thousands of vehicles.
IHS Markit predicted in its 2021 China's Autonomous Driving Market and Future Mobility Market Outlook that driverless robotaxi services like Apollo Go will account for 60% of China's $347 billion ride-hailing market by 2030.
The RT6 features Level 4 autonomous driving capability, meaning that no human intervention is ever necessary for safe operation. Zhenyu Li, senior corporate vice president of Baidu and general manager of Intelligent Driving Group (IDG), said the autonomous driving capabilities of Apollo RT6 is equivalent to a skilled human driver with 20 years of experience.
Since the Apollo Go vehicles are designed to operate without safety drivers, they're backed by a 5G-powered "Remote Driving Service". It allows a human operator to take over control of the vehicle remotely in the event the software encounters any unexpected obstacles during the trip, such as a stalled vehicle or lane closure due to construction.
To support Level 4 autonomous driving, the RT6 features 1,200 TOPS (trillions of operations per second) of computing power and 38 onboard sensors for safely navigating in complex urban environments. The exterior of the RT6 features a revolutionary look that seamlessly integrates all of the vehicle sensors for self-driving on the sunroof alongside interactive lights.
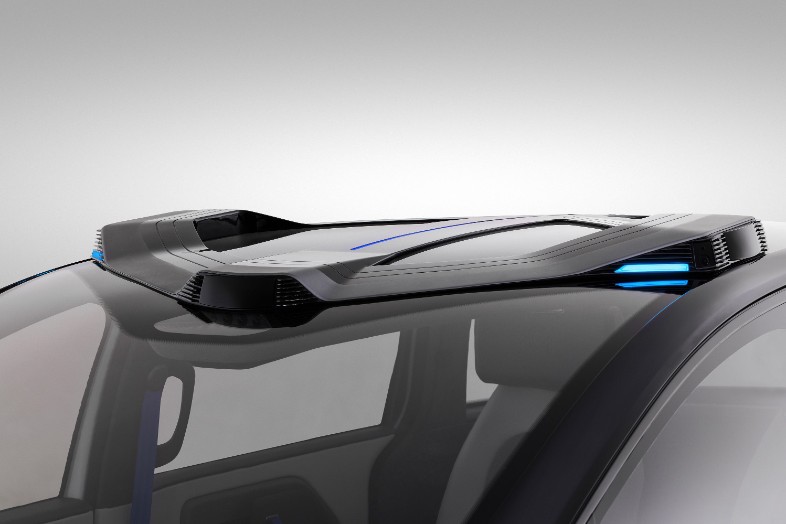
The sensors for autonomous driving are mounted on the roof of the RT6.
The sensor suite of the RT6 includes 8 lidars and 12 cameras, to obtain highly accurate, long-range perception 360 degrees around the vehicle. The safety and reliability of Apollo RT6 robotaxis are backed by a massive trove of real-world data that's being used to improve the software for autonomous driving.
The vast trove of data was collected by Baidu's fleet of autonomous vehicles that traveled over 32 million kilometers (~20 million miles) on public roads with zero accidents.
The production costs per unit of the RT6 is also extremely low at RMB 250,000 (~$37,000), which will help accelerate the deployment of autonomous vehicles at scale in China and make autonomous mobility services more affordable and accessible to the public.
"This massive cost reduction will enable us to deploy tens of thousands of AVs across China," said Robin Li, Co-founder and CEO of Baidu. "We are moving towards a future where taking a robotaxi will be half the cost of taking a taxi today."
Baidu is already the world's largest robotaxi service provider. Since its initial launch in 2020, the Apollo Go ride-hailing service has expanded to 10 cities in China and provided more than 1 million rides.
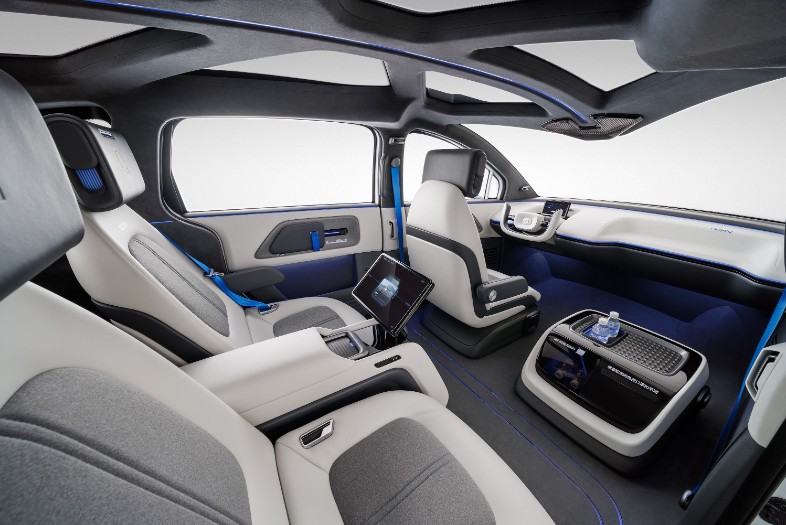

In April, Baidu received the first-ever permits in China authorizing the company to provide fully-driverless ride-hailing services to the public in Beijing, meaning that no safety drivers will be present in the Apollo Go vehicles.
It represented a benchmark achievement in the autonomous mobility industry and showed the strength of Baidu's technology. The complex and crowded streets of Beijing are some of the world's most challenging environments for a self-driving vehicle to operate in.
Baidu has been working on autonomous driving technology since 2014. In 2017, the company launched its open Apollo autonomous driving platform, which is designed to speed up the development of self-driving technology through collaboration with industry partners.
Since then, the Apollo platform has come to be regarded as the "Android of the Automotive Industry." It's the largest open-source autonomous driving platform in the world, according to Baidu.
Baidu is now working with over 200 industry partners as part of Apollo, including automakers BMW, Daimler and Volkswagen, and hardware manufacturers Intel and Nvidia.
At Baidu World 2021 held last August, company CEO Robin Li unveiled his vision for mobility of the future in the form of a futuristic "robocar" designed to make autonomous vehicles more accessible to the broader public. The robocar is capable of level 5 autonomous driving, meaning that no human intervention is ever required.
Baidu's concept robocar features automated gull-wing doors and a transparent glass roof to make the interior feel more spacious for passengers. For passenger comfort, the interior features zero-gravity seats, a large curved intelligent display and control pad.
Other features include voice and facial recognition and advanced AI technology. The robocar can analyze the internal and external surroundings and make predictive suggestions to proactively serve the needs of its passengers, according to Baidu.
Li believes that vehicles in the future will be more like "intelligent robots" rather than passenger vehicles. He predicts that these vehicles will "move, communicate and learn" using artificial intelligence.
In January, Baidu's new joint venture intelligent electric vehicle company JIDU announced it closed on $400 million in Series A financing. JiDU is backed by technology company Baidu and Chinese automaker Geely, which is the parent company of Swedish automaker Volvo Cars.
JiDU's mission is to create and design a "human-centric, smart robotic vehicle with AI-powered human-machine interaction technology". The vehicle will have the innate ability to learn and progress while delivering superior autonomous driving capabilities.
JIDU's first model will use the powerful NVIDIA DRIVE Orin system-on-a-chip (SoC) to support L4 autonomous driving capabilities. Baidu says the vehicle's intelligent autonomous driving system will be able to handle all driving scenarios, from highways to busy urban streets. The autonomous driving system's software and algorithms were jointly developed by JiDU and Baidu.
-


Ford is Testing a New Robotic Charging Station to Assist Drivers of EVs With Disabilities
-


Ford Raises the Prices of the F-150 Lightning Electric Pickup Due to Rising Raw Material Costs
-


The BMW 7-Series to Feature HD Live Maps From HERE Technologies for Hands-Free Highway Driving in North America at Speeds up to 80 MPH
-


AutoX to Use the 'Eyeonic Vision Sensor' from California-based SiLC Technologies for its Robotaxi Fleet in China
-


LG Develops ‘Invisible’ Speaker Sound Technology That Could Revolutionize In-Vehicle Audio
-


Researchers at South Korea’s Chung-Ang University Develop a ‘Meta-Reinforcement’ Machine Learning Algorithm for Traffic Lights to Improve Vehicle Throughput
-
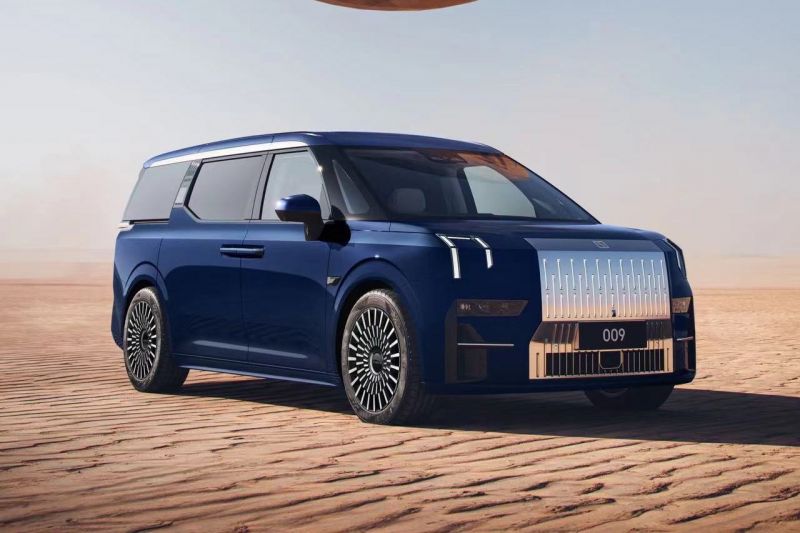


Zeekr’s New 009 Electric Passenger Van is the World’s First EV to Feature CATL’s Advanced ‘Qilin’ Battery With a Range of 510 Miles
-
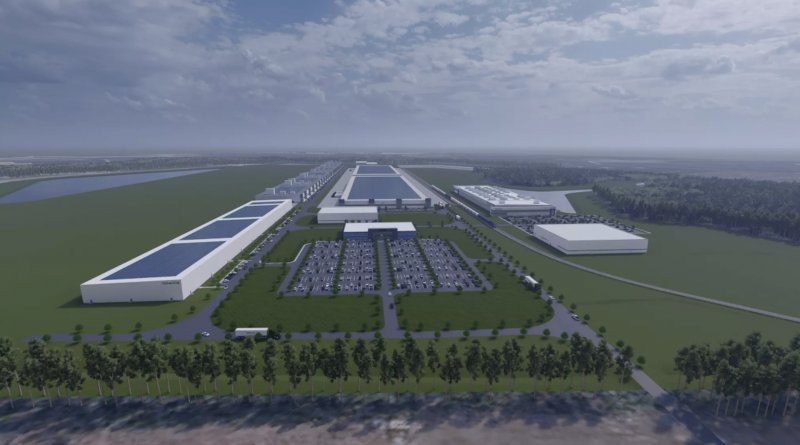


Redwood Materials is Building an Electric Vehicle Battery Recycling Facility in South Carolina
- Toyota’s Redesigned Prius May Get More Drivers Behind the Wheel of a Hybrid Vehicle
- Consumer Reports Survey Finds Roughly 28% of Respondents Don't Want to Buy an EV
- China’s Baidu Reveals the Apollo RT6, a Fully Autonomous, Production Ready Level-4 Robotaxi with Removable Steering Wheel
- Federal Tax Credit on EVs Still Applies to American-Made Vehicles
- New Premium Electric Vehicle Brand Zeekr Is Exploring IPO Options in the U.S. or Hong Kong, According to Sources
- GM to Invest $81 Million to Hand-Build Cadillac Celestiq in Michigan
- Shares of Volvo’s EV Brand Polestar to Begin Trading on the NASDAQ After Closing on its SPAC Deal With Gores Guggenheim
- Valeo Signs Major Deal with BMW to Supply Advanced Driver Assist Hardware for the Automaker's Forthcoming 'Neue Klasse' EV Platform
- Rivian to Install Electric Vehicle Chargers in Michigan State Parks as Part of a New Partnership
- Report Claims Nissan Leaf Will Be Discontinued by 2025











 About Us
About Us Contact Us
Contact Us Careers
Careers