Nexar Releases its ‘Driver Behavioral Map Data' That Can Help Autonomous Vehicles Operate More Like Human Drivers
【Summary】Computer vision company Nexar, which developed a dash cam application that seeks to rid the world of car crashes, has released its Driver Behavioral Mapping data that can be used to create maps to train autonomous vehicles to operate more like human drivers. This crowdsourced map data, which is collected anonymously by Nexar’s AI-powered dash cams, provide additional insights on how human drivers behave on different road segments and in various weather and road conditions.
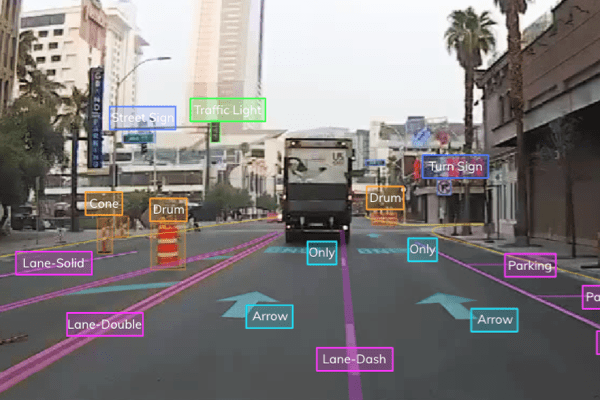
Computer vision company Nexar, which developed a dashcam application that seeks to rid the world of car crashes, has released its Driver Behavioral Mapping data that can be used to create maps to train autonomous vehicles to operate more like human drivers.
This crowdsourced map data, which is collected anonymously by Nexar's AI-powered dash cams offer up to 4K resolution and provide additional insights on how human drivers behave on different road segments and in various weather and road conditions. The map covers all 50 states in the U.S.
Nexar's AI-powered dash cams are used by both commercial and regular drivers on different roads and in varying weather conditions. This data is aggregated and overlaid on high definition (HD) base maps, which can be used by autonomous vehicles (AVs) to navigate.
Once drivers pair the Nexar dash cams with the companion app, anonymous, aggregated data captured from the cameras is used to generate a high-quality understanding of the world and the behavior of other road users – at street level. This camera data is paired with Nexar's vision-based AI, which is used to create a crowd-sourced, up to date "digital twin" of the world based on actual driving behavior.
Nexar says its the largest collector of vision data from vehicles in the U.S. with 160 millions of miles of dash cam footage gathered per month in the U.S. alone. The map data includes a constantly updated library of 4 trillion images and videos. This imagery is used to map the roads, monitor infrastructure, and alert vehicles in real time.
Nexar's vehicle-to-vehicle network connects to nearby vehicles. It can warn its users in real-time of dangerous situations happening beyond each individual driver's line of sight, such as issuing a forward collision warning to give drivers more time to react. But it can also be used to improve autonomous driving systems to better perform more like human drivers.
"A self-driving car that drives only according to a raw map would be an immediate danger due to its robotic style of driving," said Eran Shir, Co-founder and CEO of Nexar. "It's not necessarily that humans drive better than robots, it's that AVs need a lot of human data obtained by those who have driven through a particular area."

AVs require a detailed understanding of all road features as well as their semantic implications. This includes lanes, centerlines and boundaries, road markings, signs, lights and curb, construction zones and road closures. But Nexar's dash cams also capture the typical driving and movement patterns of other vehicles or pedestrians.
Nexar's Driver Behavioral Map accounts for speed, acceleration, turn probability at intersections, the probability of other vehicles changing lanes, and where pedestrians tend to cross the street. This can help AVs to better understand, measure, and benchmark safety-related behavior (stop lines, school zones etc.), as well as drive better based on road conditions and visibility.
"AVs need to sync into this behavior in order to provide the most secure and comfortable ride," said Shir.
Nexar says that AVs armed with this type of real world map data will eventually become indistinguishable from a human-driven vehicle in terms of driving style. Nexar's data-rich HD maps provide AVs with human-like driving behavior that's combined with the high level of safety of a robot driver.
By accessing a real-time record of how other vehicles drive on the same road segment at different times of day and in various weather conditions, AVs can 'see' what's ahead and have more time to react its needed.
For example, AVs can use Nexar's behavioral map data to determine when is the optimal time to switch lanes before a turn, how to decelerate when cornering, where virtual stop lines are around intersections and much more.
For those that experienced a trip in an autonomous robotaxi vehicle from Lyft, Waymo or GM's unit Cruise, the driving style of the vehicle can be robot-like and not as smooth as a human drivers. For example, AVs often brake too hard, make sudden unexpected maneuvers or take turns too fast or slow, which can make passengers in these vehicles uncomfortable.
For these ride-hailing providers, which plan to scale their robotaxi services in cities across the U.S., ensuring that their vehicles behave like human drivers will help make passengers feel more comfortable riding in an AV without a driver behind the wheel.
Nexar's behavioral map data can also be used by city planners and insurance companies to monitor how drivers navigate certain areas and behave at intersections.
Nexar envisions a world in which every vehicle is equipped with sensors and cameras and contributes to the creation and updating of HD maps for autonomous vehicles.
Earlier this month, Nexar announced it acquired Portugal-based Veniam, a developer of "intelligent networking" technology. Veniam built a technology stack that allows for the effective utilization of multiple connectivity channels by moving vehicles, including WiFii, Mesh and others.
The technology allows for the seamless upload of massive amounts of data from moving vehicles in real time, and with a much lower cost than just utilizing traditional cellular networks.
-


Ford is Testing a New Robotic Charging Station to Assist Drivers of EVs With Disabilities
-


Ford Raises the Prices of the F-150 Lightning Electric Pickup Due to Rising Raw Material Costs
-


The BMW 7-Series to Feature HD Live Maps From HERE Technologies for Hands-Free Highway Driving in North America at Speeds up to 80 MPH
-


AutoX to Use the 'Eyeonic Vision Sensor' from California-based SiLC Technologies for its Robotaxi Fleet in China
-


LG Develops ‘Invisible’ Speaker Sound Technology That Could Revolutionize In-Vehicle Audio
-
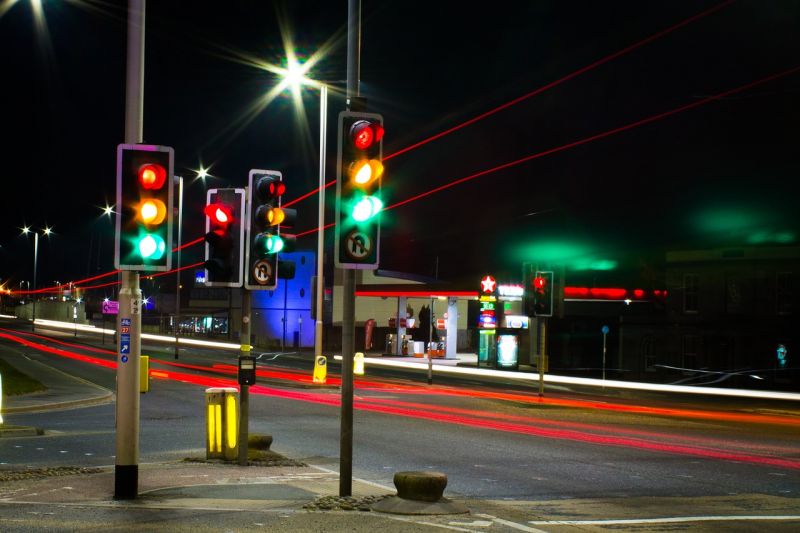


Researchers at South Korea’s Chung-Ang University Develop a ‘Meta-Reinforcement’ Machine Learning Algorithm for Traffic Lights to Improve Vehicle Throughput
-
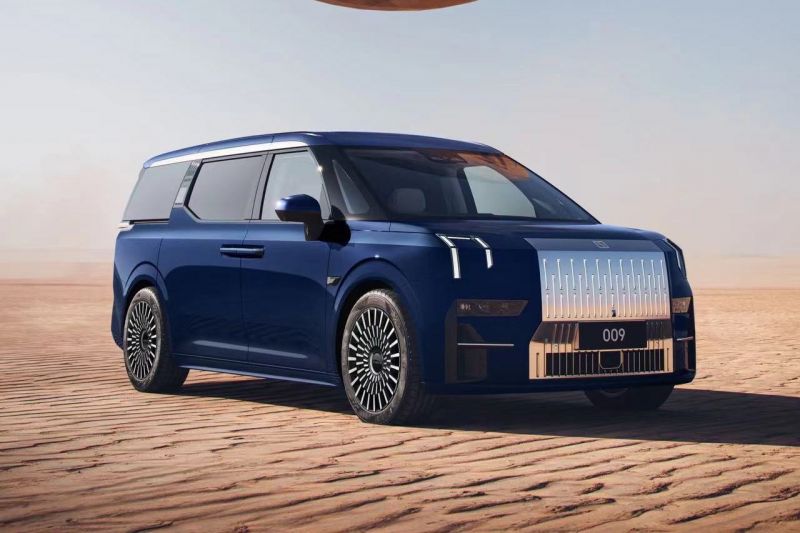


Zeekr’s New 009 Electric Passenger Van is the World’s First EV to Feature CATL’s Advanced ‘Qilin’ Battery With a Range of 510 Miles
-
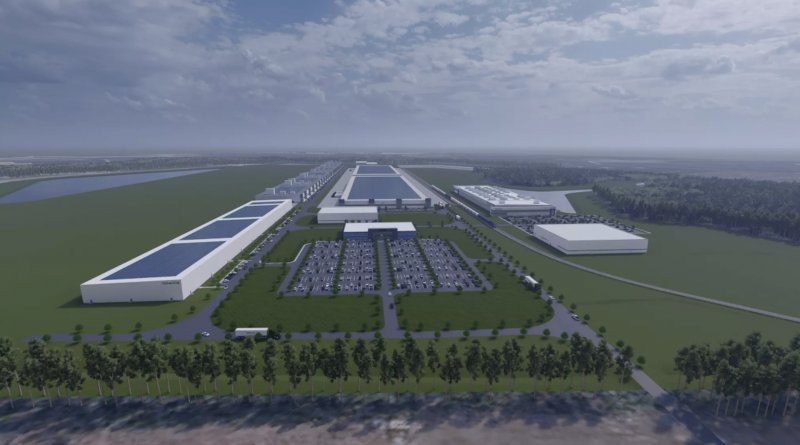


Redwood Materials is Building an Electric Vehicle Battery Recycling Facility in South Carolina
- Tesla Rival XPeng and Alibaba Cloud Set Up China’s Largest Cloud-Based Computing Center to Train Machine Learning Models for Autonomous Driving
- Premium Chinese EV Brand Zeekr Seeks to Raise $1 Billion in U.S. IPO, According to Sources
- Volkswagen Group of America President and CEO is Appointed to Lead the Automaker's New Electric Off-Road Truck Division ‘Scout’
- LG Develops ‘Invisible’ Speaker Sound Technology That Could Revolutionize In-Vehicle Audio
- China’s CATL to Supply Honda with 123 GWh of Electric Vehicle Batteries by 2030
- EV Startup VinFast is Offering 3 Years of Free EV Charging and Advanced Driver Assist System for Customers That Reserve a Vehicle Through Sept 30
- Volkswagen Breaks Ground on the First of Six European Battery Cell Factories as Part of a $20 Billion Investment
- China’s Tesla Rival XPeng Unveils its New ‘S4’ 480kW Electric Vehicle Supercharger That Can Add 125 Miles of Range in Just 5 Minutes
- Ford Unveils the F-150 Lightning Special Service Vehicle, a Fully Electric Pickup for Police Departments
- EV Charging Provider Electrify America Raises $450 Million, Siemens to Become a Minority Shareholder











 About Us
About Us Contact Us
Contact Us Careers
Careers