Siemens Invests $25 Million in Wireless Charging Company WiTricity to Develop Interoperable Standards for Cable-free EV Charging
【Summary】Industrial manufacturing company Siemens has made a $25 million strategic investment for a minority stake in WiTricity, a wireless EV charging technology developer. As part of the investment, the two companies will work together to develop interoperable standards for the rollout of wireless EV charging infrastructure.
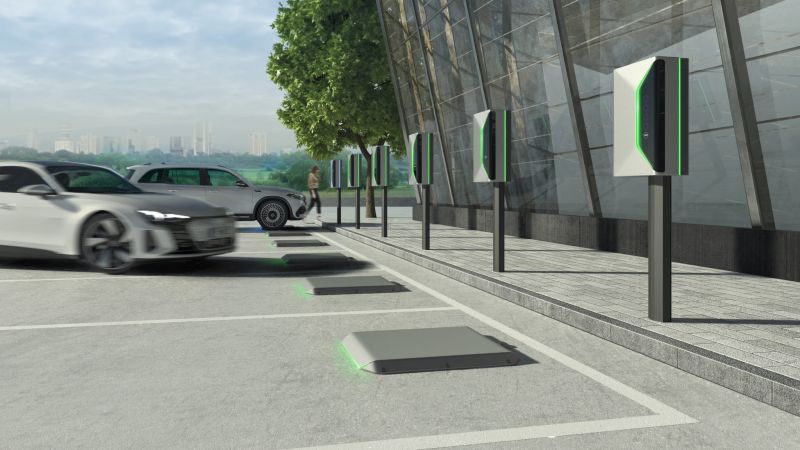

Industrial manufacturing company Siemens has made a $25 million strategic investment for a minority stake in WiTricity, a wireless EV charging technology developer. As part of the investment, the two companies will work together to develop interoperable standards for the rollout of wireless EV charging infrastructure.
Siemens and WiTricity will also work together to drive innovation in the emerging market for wireless EV charging, which is expected to grow to US$2 billion by 2028 in Europe and North America.
Watertown, Massachusetts-based WiTricity has been awarded 1,200 patents in the wireless charging field. The company is working with automakers and their suppliers to bring EV wireless charging technology to the market.
As part of the investment from Seimens, the two companies seek to bridge the gaps in the global standardization of wireless charging for electric passenger and light duty commercial vehicles, to enable interoperability between vehicles and infrastructure, as well as support market penetration.
Siemens will also become a technology license partner of WiTricity, which has been deeply collaborating with global automotive OEMs to develop proven, field-tested, interoperable wireless charging solutions for the industry.
There are currently no standards for wireless EV charging like there is for vehicles that are plugged in for charging. In North America for example, all EVs use the standard J1772 plug for Level 2 charging, with the exception of Tesla, which has its own proprietary design.
The J1772 has been adopted by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) as the standard plug for all Level 2 AC charging stations. But for wireless charging, standards have not yet been established, since the technology is still new. To address this, Seimens and WiTricity will collaborate to advance the technical development of wireless charging systems.
"Combining Siemens' global footprint and EV charging portfolio with WiTricity's innovative technology is the first step towards elevating our offering in the wireless charging space," said Markus Mildner, CEO of Siemens eMobility. "This will speed up deployment of wireless charging technology, support standardization, and advance public charging infrastructure with interoperable solutions for drivers' convenience."
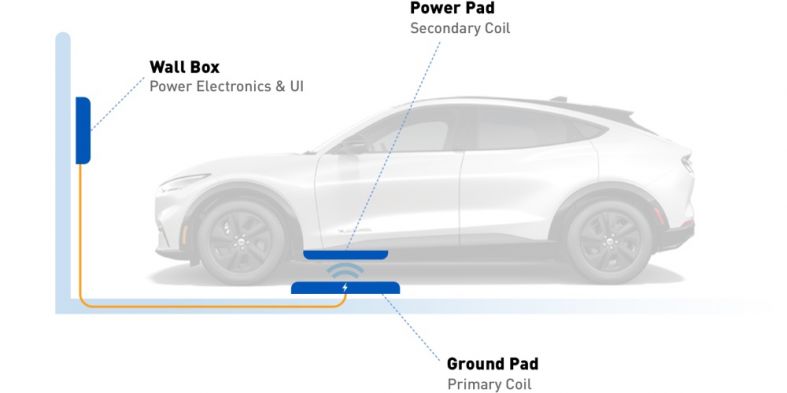
WiTricity developed a charging pad that is mounted on the ground that exchanges power with a receiving coil attached on the underside of the vehicle. The design has no moving parts or physical connectors. A driver simply parks their vehicle over the charging pad to initiate a charging session.
When a vehicle is parked over the charging pad, a magnetic field transfers energy between the charging pad and the vehicle coil to charge the vehicle's battery.
WiTricity's wireless charging technology uses resonant induction between the charger and receiver in order to provide high efficiency at a variety of ground clearances, from low to the ground sports cars to SUVs with a higher ground clearance.
"Wireless charging enables a driver to just park and walk away, returning to a charged vehicle," said Alex Gruzen, CEO of WiTricity. "Wireless charging makes EVs more appealing for individual owners and more cost-effective for commercial operators. We are excited to partner with a leader like Siemens to help drive this new world of compelling solutions."
Siemens' eMobility division offers state-of-the-art AC and DC charging hardware as well as software and services, including residential and commercial applications.
An overview of WiTricity's wireless EV charging solution.
A recent survey of more than 1,000 current and future EV owners interested in purchasing an EV in the next two years indicated that wireless charging was one of the highest-rated add-ons and a more preferred option to other amenities such as park-assist or premium audio packages.
With the rollout of fully-autonomous electric passenger vehicles, such as those that will be used in commercial ride hailing services, the wireless charging addresses one of the friction points of having to plug in a vehicle to charge. Although robotic solutions that plug in the cable are being developed by some companies, including automaker Volkswagen, wireless charging technology with no moving parts is thought to be a better and more reliable long-term solution for fleets of autonomous vehicles.
In early March, WiTricity announced plans to offer a limited beta aftermarket wireless charging upgrade package for owners of select EV models, including the Tesla Model 3. The upgrade is called "WiTricity Halo" and it's a complete end-to-end and hassle-free charging experience, drivers just park and charge.
The WiTricity Halo upgrade will deliver 11 kW wireless charging, enabling a charge rate that provides up to 35-40 miles of driving range per hour of charging time, which the company says is on par with today's Level 2 AC plug-in chargers.
WiTricity's Halo can charge a Tesla Model 3 wirelessly in less than 6 hours, which the company says is just as fast as plugging into a charger at home. WiTricity engineers are also developing a wireless charging solution for the Ford Mustang Mach-E, with more vehicles in the pipeline.
However WiTricity says that The final decision on which electric models will be selected for the Halo wireless charging upgrade has yet to be determined and will be based on customer demand, technical feasibility, and automaker support.
The WiTricity Halo setup includes three key components: the power receiver installed on the vehicle, the wall box that connects to electric power in a garage, and the charging pad that is installed on- or in-ground.
WiTricity says its Halo charging upgrade will be initially available in the U.S to owners of select EVs starting with a beta in late 2022, followed by broader availability in 2023.
The ultimate goal of Siemens' investment in WiTricity is to accelerate the advancement of wireless charging technologies together with OEMs and infrastructure partners to ensure that it's cost-effective and readily available worldwide.
-


Ford is Testing a New Robotic Charging Station to Assist Drivers of EVs With Disabilities
-


Ford Raises the Prices of the F-150 Lightning Electric Pickup Due to Rising Raw Material Costs
-


The BMW 7-Series to Feature HD Live Maps From HERE Technologies for Hands-Free Highway Driving in North America at Speeds up to 80 MPH
-


AutoX to Use the 'Eyeonic Vision Sensor' from California-based SiLC Technologies for its Robotaxi Fleet in China
-


LG Develops ‘Invisible’ Speaker Sound Technology That Could Revolutionize In-Vehicle Audio
-


Researchers at South Korea’s Chung-Ang University Develop a ‘Meta-Reinforcement’ Machine Learning Algorithm for Traffic Lights to Improve Vehicle Throughput
-


Zeekr’s New 009 Electric Passenger Van is the World’s First EV to Feature CATL’s Advanced ‘Qilin’ Battery With a Range of 510 Miles
-


Redwood Materials is Building an Electric Vehicle Battery Recycling Facility in South Carolina
- 2023 Jeep Grand Cherokee Trailhawk Now PHEV Only
- Honda's New EV Friendly Retail Plans Hint at the End of Mega Dealerships
- Volvo’s Brand Polestar Confirms That the Polestar 6 Electric Roadster Will Enter Production and Launch in 2026
- Biden Administration Announces New Standards to Make EV Chargers More Accessible
- EV Startup VinFast Simultaneously Opens Six Retail Stores in California as it Prepares to Enter the U.S. Market
- Tesla Rival XPeng and Alibaba Cloud Set Up China’s Largest Cloud-Based Computing Center to Train Machine Learning Models for Autonomous Driving
- Mercedes-Benz Begins Production of the Highly Anticipated EQS Electric SUV in Alabama
- China Has Installed Around 4.7 Million Electric Vehicle Charging Poles as of October 2022
- BMW to Test a New Battery in the iX Electric SUV Developed By Michigan Startup Our Next Energy Inc. That Can Deliver 600 Miles of Range
- Ford Looks to Have 100% of EV Sales Be Online











 About Us
About Us Contact Us
Contact Us Careers
Careers